A photovoltaic system, or solar power system, used to be practical only to companies and factories due to numerous factors. Continuous development has, however, brought progress to today’s solar power technology in terms of photovoltaic performance, size of devices and costs of installation, resulting practical use of a solar power in homes and residential buildings in form of rooftop photovoltaic system (solar rooftop). By converting solar energy into usable power supply for home appliances, this solar power system enables home users to cut down their electricity bills and contribute to the environment through an alternative source of energy.
A solar power system is comprised of two main components: the solar panels that absorb sunlight to generate direct current electricity; and the inverter that converts the electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current to make it usable for home appliances.
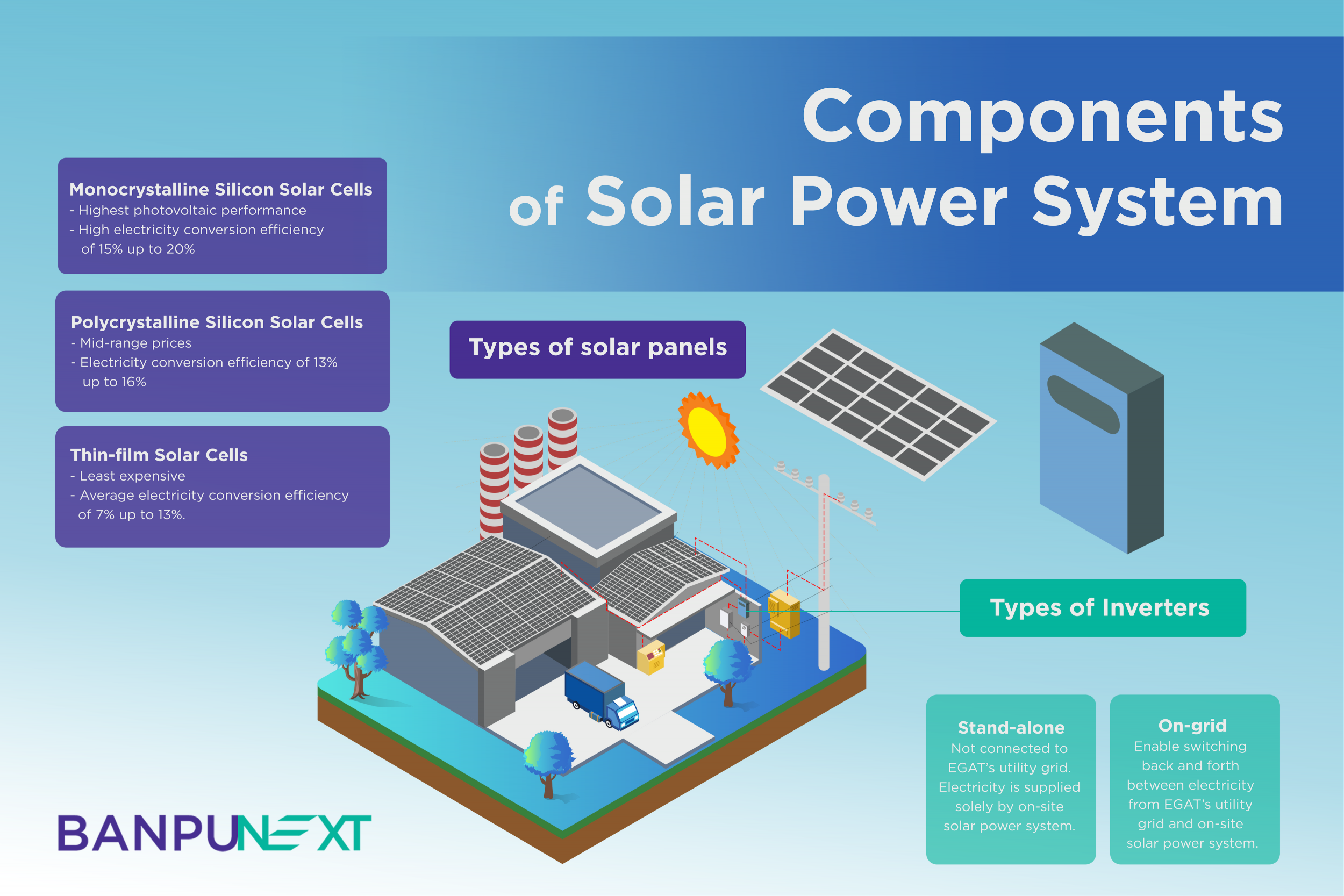
- There are many types of solar panels. The most popular type uses silicon as its semiconducting material and can be subdivided into three different types based on purity of the silicon used.
1.1 Monocrystalline silicon solar cells are made from ultrapure silicon, which gives them dark colour and the highest photovoltaic performance in comparison to other types. They provide a high conversion efficiency of 15% up to 20% and perform well even in lower light conditions. With proper maintenance and care, their service life averages more than 25 years. Due to superior efficiency, solar panels with this type of cells are the most expensive.
1.2 Polycrystalline silicon solar cells, also called multicrystalline silicon (mc-Si) solar cells, are made from liquid silicon. Due to less silicon content, polycrystalline silicon solar cells have blue color. They are less expensive and have lower photovoltaic performance than their monocrystalline counterparts. On average, they give an electricity conversion efficiency of 13% up to 16%.
1.3 Thin-film solar cells convert sunlight to electricity using thin layers of photovoltaic materials, such as amorphous silicon, which also give them different names depending on the material used. These solar cells are the least expensive type with relatively lower electricity conversion efficiency ranging from only 7% to 13%.
The information above explains why solar panels using monocrystalline silicon technology are the most popular type across industrial and household applications. Despite higher prices, they prove to be most cost-effective choice due to higher conversion efficiency and longer service life.
- Inverters can be divided into two types based on electricity delivery system.
2.1 Stand-alone system is not connected to the utility grid of Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT). The premises are therefore powered solely by electricity generated on-site by the solar power system, using storage battery to enable nighttime power supply.
2.2 On-grid system is connected to EGAT’s utility grid, which enable switching back and forth between grid and local power supply. Electricity from on-site solar power system is used only when the system generates sufficient power supply, allowing reduced use of grid power. On-grid solar power systems are more popular today because they free users from worries over insufficient supply of power generated and kept in storage battery by the solar power system, as well as on cloudy days or in other unfavorable conditions when solar power generation may fall short of demand.
If a solar power system is being planned, give prioritized thoughts to the location, direction, position and building structure. The best approach is to seek advice from an expert or a specialized solar power system provider to ensure full system efficiency, proper system inspection and maintenance, best value and the most sustainable installation.